C++
Important Links
Data Types in C++
They are used to define type of variables and contents used. Data types define the way you use storage in the programs you write.
There are 4 types of data types in C++ language.
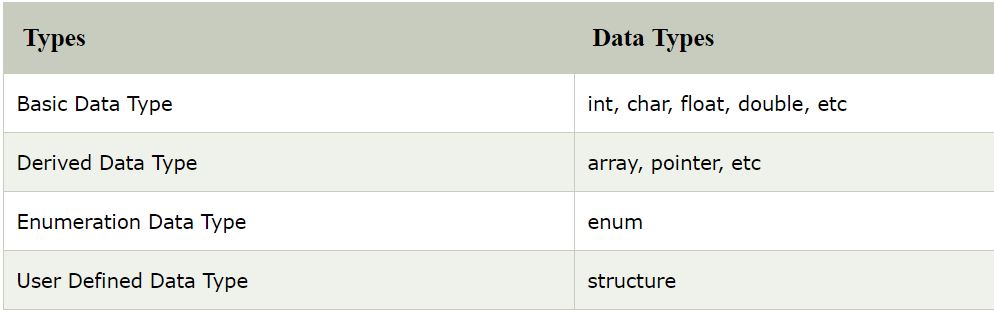

Enum as Data type :-
Enumerated type declares a new type-name and a sequence of value containing identifiers which has values starting from 0 and incrementing by 1 every time.
enum day(mon, tues, wed, thurs, fri) d;
Here an enumeration of days is defined with variable d. mon will hold value 0, tue will have 1 and so on. We can also explicitly assign values, like, enum day(mon, tue=7, wed);. Here, mon will be 0, tue is assigned 7, so wed will have value 8.
enum day(mon, tues, wed, thurs, fri) d;
Here an enumeration of days is defined with variable d. mon will hold value 0, tue will have 1 and so on. We can also explicitly assign values, like, enum day(mon, tue=7, wed);. Here, mon will be 0, tue is assigned 7, so wed will have value 8.
Modifiers :-
Specifiers modify the meanings of the predefined built-in data types and expand them to a much larger set. There are four data type modifiers in C++, they are :
long
short
signed
unsigned
long and short modify the maximum and minimum values that a data type will hold.
A plain int must have a minimum size of short.
Size hierarchy : short int < int < long int
Size hierarchy for floating point numbers is : float < double < long double
long float is not a legal type and there are no short floating point numbers.
Signed types includes both positive and negative numbers and is the default type.
Unsigned, numbers are always without any sign, that is always positive.