what is Array?
In C language, array is a collection of similar data types. An array is defined as finite ordered collection of homogenous data, stored in contiguous memory locations.
Here the words :-
Array in C language is a collection or group of elements (data). All the elements of c array are homogeneous (similar). It has contiguous memory location.
Advantage of C Array :-
Disadvantage of C Array :-
Declaring an Array :-
data-type variable-name[array-size];
/* Example of array declaration */
int arr[10];
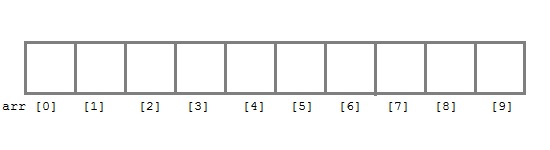
Here int is the data type, arr is the name of the array and 10 is the size of array. It means array arr can only contain 10 elements of int type.
Index of an array starts from 0 to size-1 i.e first element of arr array will be stored at arr[0] address and the last element will occupy arr[9].
Initialization of an Array :-
After an array is declared it must be initialized. Otherwise, it will contain garbage value(any random value). An array can be initialized at either compile time or at runtime.
marks[1]=50;
marks[2]=60;
marks[3]=75;
marks[4]=65;
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int i=0;
int marks[5];//declaration of array
marks[0]=80;//initialization of array
marks[1]=60;
marks[2]=70;
marks[3]=85;
marks[4]=75;
//traversal of array
for(i=0;i<5;i++){
printf("%d \n",marks[i]);
}//end of for loop
return 0;
}
Output :-
60
70
85
75
Compile time Array initialization :-
data-type array-name[size] = { list of values };
/* Here are a few examples */
int marks[4]={ 67, 87, 56, 77 }; // integer array initialization
float area[5]={ 23.4, 6.8, 5.5 }; // float array initialization
int marks[4]={ 67, 87, 56, 77, 59 }; // Compile time error
Compile time Array initialization :-
void main()
{
int i;
int arr[] = {2, 3, 4}; // Compile time array initialization
for(i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++)
{
printf("%d\t",arr[i]);
}
}
Output
2 3 4
Runtime Array initialization :-
#include<
{
int arr[4];
int i, j;
printf("Enter array element");
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr[i]); //Run time array initialization
}
for(j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
printf("%d\n", arr[j]);
}
}
Declaration with Initialization :-
int marks[5]={20,30,40,50,60};
In such case, there is no requirement to define size. So it can also be written as the following code.
int marks[]={20,30,40,50,60};
int main(){
int i=0;
int marks[5]={20,30,40,50,60};//declaration and initialization of array
//traversal of array
for(i=0;i<5;i++){
printf("%d \n",marks[i]);
}
return 0;
}
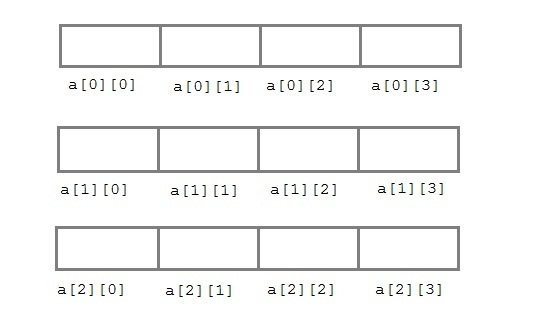
Two Dimensional Array in C :-
The two dimensional array in C language is represented in the form of rows and columns, also known as matrix. It is also known as array of arrays or list of arrays.
The two dimensional, three dimensional or other dimensional arrays are also known as multidimensional arrays.
/* Example */
int a[3][4];
Initialization of 2D Array
int disp[2][4] = {
{10, 11, 12, 13},
{14, 15, 16, 17}
};
OR
int disp[2][4] = { 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17};
int arr[][3] = {
{0,0,0},
{1,1,1}
};
Note: We have not assigned any row value to our array in the above example. It means we can initialize any number of rows. But, we must always specify number of columns, else it will give a compile time error. Here, a 2*3 multi-dimensional matrix is created.
int abc[2][2] = {1, 2, 3 ,4 }
/* Valid declaration*/
int abc[][2] = {1, 2, 3 ,4 }
/* Invalid declaration – you must specify second dimension*/
int abc[][] = {1, 2, 3 ,4 }
/* Invalid because of the same reason mentioned above*/
int abc[2][] = {1, 2, 3 ,4 }
Runtime initialization of a two dimensional Array
void main()
{
int arr[3][4];
int i, j, k;
printf("Enter array element");
for(i = 0; i < 3;i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr[i][j]);
}
}
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
printf("%d", arr[i][j]);
}
}
}
int main(){
int i=0,j=0;
int arr[4][3]={{1,2,3},{2,3,4},{3,4,5},{4,5,6}};
//traversing 2D array
for(i=0;i<4;i++){
for(j=0;j<3;j++){
printf("arr[%d] [%d] = %d \n",i,j,arr[i][j]);
}//end of j
}//end of i
return 0;
}
output :-
arr[0][1] = 2
arr[0][2] = 3
arr[1][0] = 2
arr[1][1] = 3
arr[1][2] = 4
arr[2][0] = 3
arr[2][1] = 4
arr[2][2] = 5
arr[3][0] = 4
arr[3][1] = 5
arr[3][2] = 6
Passing Array to Function in C :-
functionname(arrayname);//passing array
There are 3 ways to declare function that receives array as argument. :-
return_type function(type arrayname[])
Declaring blank subscript notation [] is the widely used technique.
Second way:
return_type function(type arrayname[SIZE])
Optionally, we can define size in subscript notation [].
Third way:
return_type function(type *arrayname)
passing array to function :-
int minarray(int arr[],int size){
int min=arr[0];
int i=0;
for(i=1;i
min=arr[i];
}
}//end of for
return min;
}//end of function
int main(){
int i=0,min=0;
int numbers[]={4,5,7,3,8,9};//declaration of array
min=minarray(numbers,6);//passing array with size
printf("minimum number is %d \n",min);
return 0;
}
output :-
Previous Next
Trending Tutorials
0.0 / 5
0 Review
 What is C
What is C 