What is operators?
An Operator is a symbol that is used to perform certain mathematical or logical manipulation (operations). Operators are used in progam to manipulate data and variables.
There are following types of operators to perform different types of operations in C language.
Arithmetic Operators :-
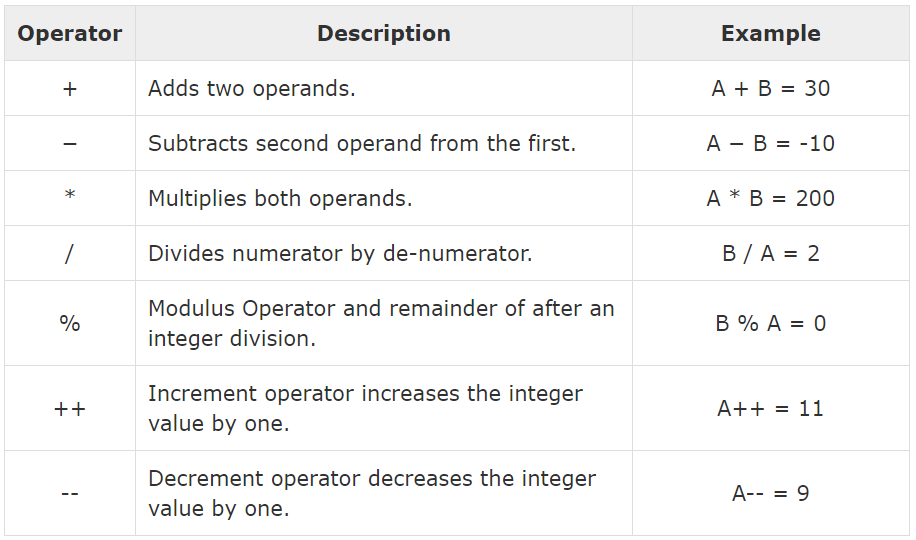
a%b , here a and b are variable and are known as operands. The modulo division operator can't be used in flooting point data.
Example :-
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 15;
int sum = a + b;
printf("sum = %d", sum);
}
Relational Operators :-
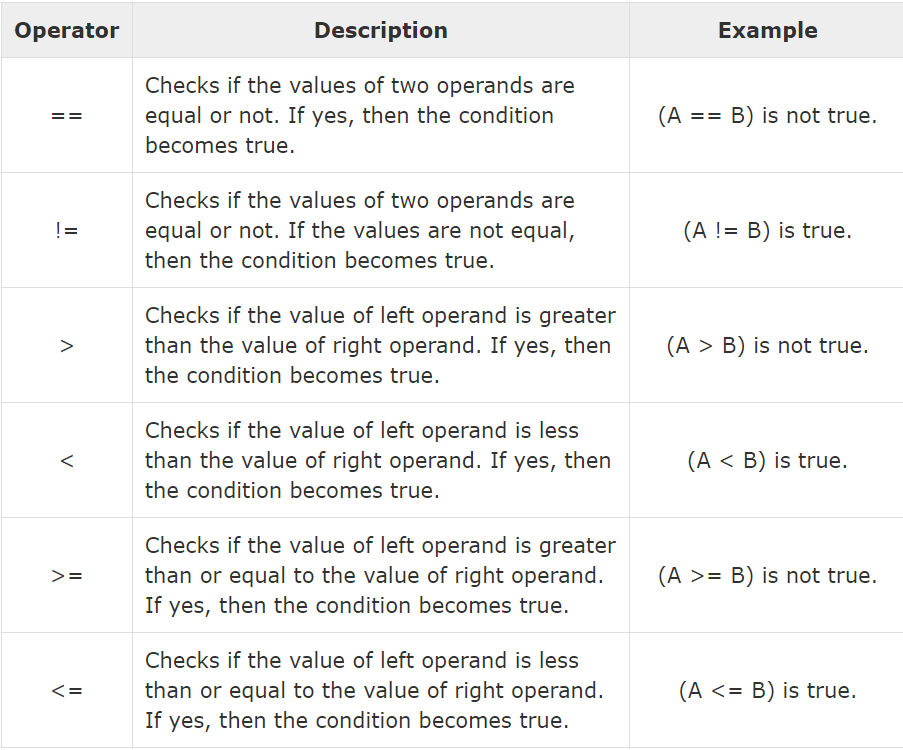
These operators are used to distinguish between two values depending on their relations. These operators provides the relationship between the two expressions. if the relation is true then it returns a value 1 otherwise 0 for flase relation.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
clrscr();
printf("\n 10!=10 : %5d", 10!=10);
printf("\n 10==10 : %5d", 10==10);
printf("\n 10>=10 : %5d", 10>=10);
}
output :-
condition : return values
10!=10 : 0
10==10 : 1
10>=10 : 1
#include <stdio.h> main() { int a = 21; int b = 10; int c ; if( a == b ) { printf("a is equal to b\n" ); } else { printf("a is not equal to b\n" ); } if ( a < b ) { printf("a is less than b\n" ); } else { printf("a is not less than b\n" ); } if ( a > b ) { printf("a is greater than b\n" ); } else { printf("a is not greater than b\n" ); } /* Lets change value of a and b */ a = 5; b = 20; if ( a <= b ) { printf("a is either less than or equal to b\n" ); } if ( b >= a ) { printf("b is either greater than or equal to b\n" ); } }
Logical Operators in C :-

The logical relationship between the two expressions are checked with logical operators. using these operator two expression can be joined. after checking the condition it provides logical true (1) or false (0) status.
when you wnant to test more than one condition and make decision.
&& :- both condition are ture.
|| :- Either one condition is true or false.
! : if condition true return flase. and condition false return true.
#include
main() {
int a = 5;
int b = 20;
int c ;
if ( a && b ) {
printf("Condition is true\n" );
}
if ( a || b ) {
printf("Condition is true\n" );
}
/* lets change the value of a and b */
a = 0;
b = 10;
if ( a && b ) {
printf("Condition is true\n" );
} else {
printf("Condition is not true\n" );
}
if ( !(a && b) ) {
printf("Condition is true\n" );
}
}
Assignment Operators :-
operator : standard operations
a = a+1 : a += 1
a = a-1 : a -= 1
a = a*1 : a *= 1
a = a/1 : a /= 1
a = a%1 : a %= 1
conditional operator or ternary operator :-
The conditional operator contains a condition followed by two statements or values. if the condition is true the first statement is executed otherwise the second statement.
The conditional operator (?) and (:) are sometimes called Ternary operator because they take three arguments.
Syntax :-
void main()
{
printf("Result = %s", 2==3?yes:No);
}
Bitwise operator :-
'C' Support six bit operators. These operators can operate only on an integer operands such as int, char, short, long int etc. These operators are used for testing bits or shifting them right or left. bitwise operator may not be applied to float or double.


#include <stdio.h>
main() {
unsigned int a = 60; /* 60 = 0011 1100 */
unsigned int b = 13; /* 13 = 0000 1101 */
int c = 0;
c = a & b; /* 12 = 0000 1100 */
printf("Line 1 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a | b; /* 61 = 0011 1101 */
printf("Line 2 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a ^ b; /* 49 = 0011 0001 */
printf("Line 3 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = ~a; /*-61 = 1100 0011 */
printf("Line 4 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a << 2; /* 240 = 1111 0000 */
printf("Line 5 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a >> 2; /* 15 = 0000 1111 */
printf("Line 6 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
}
output :-
Line 1 - Value of c is 12 Line 2 - Value of c is 61 Line 3 - Value of c is 49 Line 4 - Value of c is -61 Line 5 - Value of c is 240 Line 6 - Value of c is 15
Previous Next
Trending Tutorials
0.0 / 5
0 Review
 What is C
What is C 