What is Node.Js Modules?
Module in Node.js is a simple or complex functionality organized in single or multiple JavaScript files which can be reused throughout the Node.js application.
Each module in Node.js has its own context, so it cannot interfere with other modules or pollute global scope. Also, each module can be placed in a separate .js file under a separate folder.
Module Types
Node.js includes three types of modules:
Core Modules
The core modules include minimum functionalities of Node.js. These core modules are compiled into its binary distribution and load automatically when Node.js process starts. However, you need to import the core module first in order to use it in your application.
File Name :
The following table lists some of the important core modules in Node.js.
http :- http module includes classes, methods and events to create Node.js http server.url :-url module includes methods for URL resolution and parsing.
querystring :-querystring module includes methods to deal with query string.
path :-path module includes methods to deal with file paths.
fs :-fs module includes classes, methods, and events to work with file I/O.
util :- util module includes utility functions useful for programmers.
Loading Core Modules
you first need to import it using require() function
specify the module name in the require() function. The require() function will return an object, function, property or any other JavaScript type, depending on what the specified module returns.
Example
File Name : example.js
var server = http.createServer(function(req, res){
//write code here
});
server.listen(8080);
require() function returns an object because http module returns its functionality as an object, you can then use its properties and methods using dot notation e.g. http.createServer().
HTTP Module
Node.js has a built-in module called HTTP, which allows Node.js to transfer data over the Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP). To include the HTTP module, use the require() method:
The Node.js framework is mostly used to create web server based applications. The node.js used to create web servers which can serve content to users.
If a request is made through the browser on this port no 8080, then server application will send a ‘result’ response to the client.
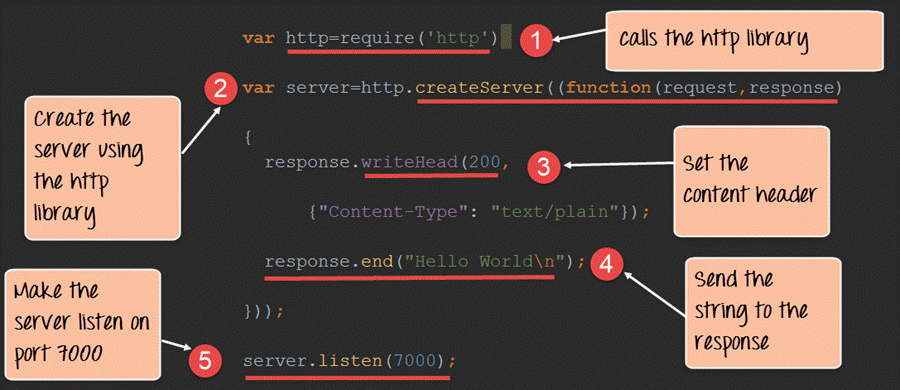
Add an HTTP Header
If the response from the HTTP server is to be displayed as HTML, you should include an HTTP header with the correct content type:
File Name : sana.js
http.createServer(function (req, res) {
// add a HTTP header:
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
res.write('Hello Sana!');
res.end();
}).listen(8080);
The first argument of the res.writeHead() method is the status code, 200 means that all is OK, the second argument is an object containing the response headers.
File Name :
Create Your Own Modules
ou can create your own modules.
File Name : myfirstmodule.js
exports.myDateTime = function () {
return Date();
};
Use the exports keyword to make properties and methods available outside the module file.
Include Your Own Module
The HTTP module can create an HTTP server that listens to server ports and gives a response back to the client. Use the createServer() method to create an HTTP server:
The function passed into the http.createServer() method, will be executed when someone tries to access the computer on port 8080.
var dt = require('./myfirstmodule');
http.createServer(function (req, res) {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
res.write("The date and time are currently: " + dt.myDateTime());
res.end();
}).listen(8080);
Read the Query String
The function passed into the http.createServer() has a req argument that represents the request from the client, as an object
This object has a property called "url" which holds the part of the url that comes after the domain name:
File Name : sana.js
http.createServer(function (req, res) {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
res.write(req.url);
res.end();
}).listen(8080);
Split the Query String
var url = require('url');
http.createServer(function (req, res) {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
var q = url.parse(req.url, true).query;
var txt = q.year + " " + q.month;
res.end(txt);
}).listen(8080);
GET Requests in Node.js
GET Request to get the data from another site in Node.js. To make a Get request in the node.js, we need to first have the request module installed.
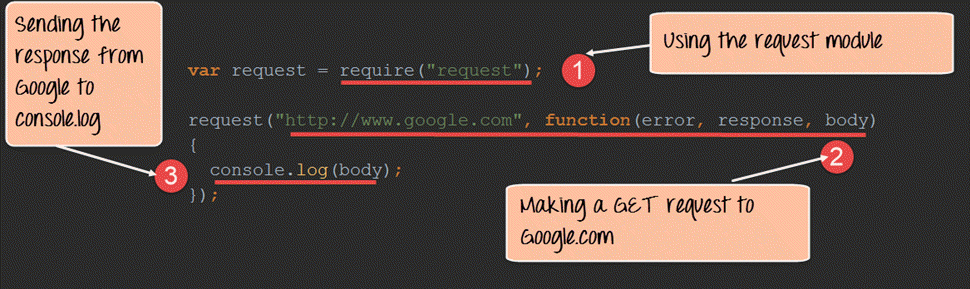
We are making a GET Request to www.ittutorial.in and subsequently calling a function when a response is received. When a response is received the parameters(error, response, and body) will have the following values
In this, we are just writing the content received in the body parameter to the console.log file. So basically, whatever we get by going to www.ittutorial.in will be written to the console.log.
File Name :
request("http://www.ittutorial.in",function(error,response,body)
{
console.log(body);
});
Previous Next
Trending Tutorials
0.0 / 5
0 Review
 Why use node.js
Why use node.js 