C Tutorials
- What is C?
- History Of C?
- Feature of C?
- How to Install C?
- How to write c program?
- First c program
- Flow of C program
- printf() and scanf() in C
- C Program Structure
- Variables in C
- Data Types in C
- Keywords in C
- C Operators
- Comments in C
- Escape Sequence in C
- Escape Sequence in C
- Constants in C
- C - Storage Classes
- C - Decision Making
- Switch statement in C
- C Loops
- Loop Control Statements
- Type Casting in C
- functions in C
- call by value Or call by reference
- Recursion in C
- Storage Classes in C
- Array
- String
- Pointer
- Pointer And Array
- Pointer with function
- Structure
- Union
- File Handling
- Preprocessor Directives
Important Links
Call by value and call by reference in C
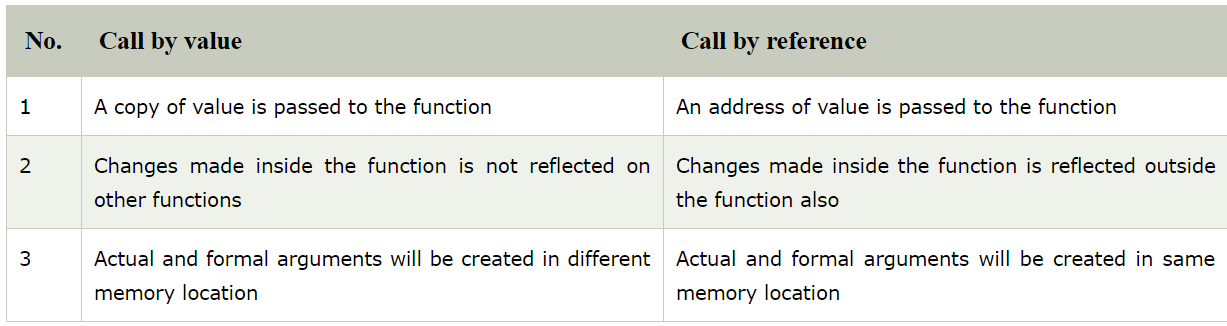
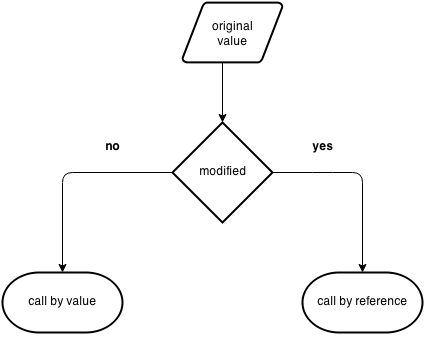
There are two ways to pass value or data to function in C language: call by value and call by reference. Original value is not modified in call by value but it is modified in call by reference.
Call by value in C :-
In call by value, original value is not modified.
Calling a function by value means, we pass the values of the arguments which are stored or copied into the formal parameters of the function. Hence, the original values are unchanged only the parameters inside the function changes.
In call by value, value being passed to the function is locally stored by the function parameter in stack memory location. If you change the value of function parameter, it is changed for the current function only. It will not change the value of variable inside the caller method such as main().
#include<stdio.h>
void calc(int x);
int main()
{
int x = 10;
calc(x);
// this will print the value of 'x'
printf("\nvalue of x in main is %d", x);
return 0;
}
void calc(int x)
{
// changing the value of 'x'
x = x + 10 ;
printf("value of x in calc function is %d ", x);
}
Output
value of x in main is 10
Example
#include<stdio.h>
void change(int num) {
printf("Before adding value inside function num=%d \n",num);
num=num+100;
printf("After adding value inside function num=%d \n", num);
}
int main() {
int x=100;
printf("Before function call x=%d \n", x);
change(x);//passing value in function
printf("After function call x=%d \n", x);
return 0;
}
Output :-
Before adding value inside function num=100
After adding value inside function num=
After function call x=100
Note :-
Call by reference in C :-
In call by reference we pass the address(reference) of a variable as argument to any function. When we pass the address of any variable as argument, then the function will have access to our variable, as it now knows where it is stored and hence can easily update its value.
In this case the formal parameter can be taken as a reference or a pointer in both the cases they will change the values of the original variable.
Example
#include<stdio.h>
void calc(int *p); // functin taking pointer as argument
int main()
{
int x = 10;
calc(&x); // passing address of 'x' as argument
printf("value of x is %d", x);
return(0);
}
void calc(int *p) //receiving the address in a reference pointer variable
{
/*
changing the value directly that is
stored at the address passed
*/
*p = *p + 10;
}
output
Example
#include<stdio.h>
void change(int *num) {
printf("Before adding value inside function num=%d \n",*num);
(*num) += 100;
printf("After adding value inside function num=%d \n", *num);
}
int main() {
int x=100;
printf("Before function call x=%d \n", x);
change(&x);//passing reference in function
printf("After function call x=%d \n", x);
return 0;
}
output
Before adding value inside function num=100
After adding value inside function num=200
After function call x=200
Difference between call by value and call by reference in c