C Tutorials
- What is C?
- History Of C?
- Feature of C?
- How to Install C?
- How to write c program?
- First c program
- Flow of C program
- printf() and scanf() in C
- C Program Structure
- Variables in C
- Data Types in C
- Keywords in C
- C Operators
- Comments in C
- Escape Sequence in C
- Escape Sequence in C
- Constants in C
- C - Storage Classes
- C - Decision Making
- Switch statement in C
- C Loops
- Loop Control Statements
- Type Casting in C
- functions in C
- call by value Or call by reference
- Recursion in C
- Storage Classes in C
- Array
- String
- Pointer
- Pointer And Array
- Pointer with function
- Structure
- Union
- File Handling
- Preprocessor Directives
Important Links
Home » Recursion in C »
Recursion in C
When function is called within the same function, it is known as recursion in C. The function which calls the same function, is known as recursive function.
A function that calls itself, and doesn't perform any task after function call, is know as tail recursion. In tail recursion, we generally call the same function with return statement. An example of tail recursion is given below.
recurfun(){
recurfun();//calling self function
}
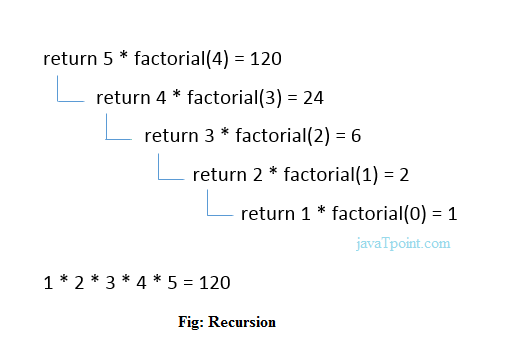
Example of tail recursion in C :-
#include<stdio.h>
int factorial (int n)
{
if ( n < 0)
return -1; /*Wrong value*/
if (n == 0)
return 1; /*Terminating condition*/
return (n * factorial (n -1));
}
int main(){
int fact=0;
fact=factorial(5);
printf("\n factorial of 5 is %d",fact);
return 0;
}
int factorial (int n)
{
if ( n < 0)
return -1; /*Wrong value*/
if (n == 0)
return 1; /*Terminating condition*/
return (n * factorial (n -1));
}
int main(){
int fact=0;
fact=factorial(5);
printf("\n factorial of 5 is %d",fact);
return 0;
}
Output :-
factorial of 5 is 120
Output :-
factorial of 5 is 120