what is SubQuery?
A Query contains another query is called subquery. subquery is called an inner query while the query that contains the subquery is called an outer query. A subquery can be used anywhere that expression is used and must be closed in parentheses.
subquery is a query within another query such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE. subquery used with the operators like =, <, >, >=, <=, IN, BETWEEN, etc.
Rules:-
Subqueries must be enclosed within parentheses.
A subquery can have only one column in the SELECT clause, unless multiple columns are in the main query for the subquery to compare its selected columns.
An ORDER BY command cannot be used in a subquery, although the main query can use an ORDER BY. The GROUP BY command can be used to perform the same function as the ORDER BY in a subquery.
Subqueries that return more than one row can only be used with multiple value operators such as the IN operator.
The BETWEEN operator cannot be used with a subquery. However, the BETWEEN operator can be used within the subquery.
The inner query executes first before its outer query so that the results of an inner query can be passed to the outer query.
Example :-
SELECT columnname [, columnname ] FROM table1 [, table2 ] WHERE columnname OPERATOR
(SELECT columnname [, columnname ] FROM table1 [, table2 ] [WHERE]) ....
SELECT Name, MobileNo FROM itechxpert WHERE cityname IN (SELECT cityname FROM state WHERE country = 'India');
The subquery returns all city codes of the state located in the India.
The outer query selects the name and mobileno of employees who work in the state whose city codes are in the result set returned by the subquery.
When the query is executed, the subquery runs first and returns a result set. Then, this result set is used as an input for the outer query.
SELECT
customerID,
checkNumber,
amount
FROM
payments
WHERE
amount = (SELECT MAX(amount) FROM payments);
SELECT
customerNumber,
checkNumber,
amount
FROM
payments
WHERE
amount > (SELECT
AVG(amount)
FROM
payments);
SELECT
customerName
FROM
customers
WHERE
customerNumber NOT IN (SELECT DISTINCT
customerNumber
FROM
orders);
SELECT category_name FROM categories WHERE category_id =( SELECT MIN(category_id) from movies);
SELECT full_names,contact_number FROM members WHERE membership_number IN (SELECT membership_number FROM movierentals WHERE return_date IS NULL );
MySQL supports three types of subqueries, scalar, row and table subqueries.
Scalar sub queries only return a single row and single column.
Row sub queries only return a single row but can have more than one column.
Table subqueries can return multiple rows as well as columns.
Subqueries can also be used in INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE queries.
SELECT emp_name, city, income FROM employees WHERE emp_id IN (SELECT emp_id FROM employees);
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE emp_id IN (SELECT emp_id FROM employees WHERE income > 200000);
SELECT Name, City FROM student WHERE City NOT IN ( SELECT City FROM student2 WHERE City='Ara');
SELECT *
FROM itechxpert
WHERE emp_id IN (SELECT emp_id
FROM itechxpert
WHERE SALARY > 59000) ;
How to use Subqueries with the INSERT Statement?
The INSERT statement uses the data returned from the subquery to insert into another table.
INSERT INTO itechxpert SELECT * FROM ittutorial WHERE author_id IN (SELECT author_id FROM ittutorial) ;
How to use Subqueries with the UPDATE Statement?
UPDATE itechxpert SET SALARY = SALARY * 2 WHERE AGE IN (select age from emp WHERE age >= 30 );
How to use Subqueries with the DELETE Statement?
DELETE FROM itechxpert WHERE AGE IN (SELECT AGE FROM ittutorial WHERE AGE >= 30 );
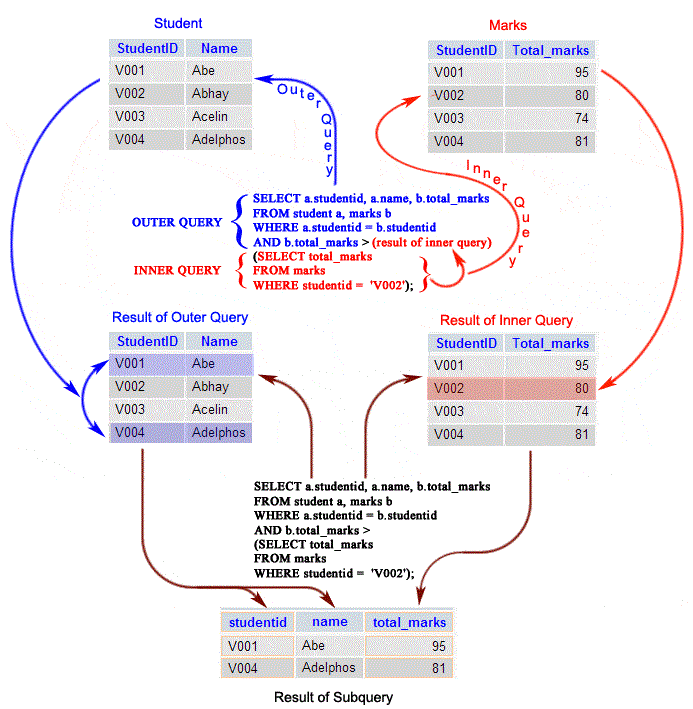
Example :-
SELECT a.studentid, a.name, b.total_marks
FROM student a, marks b
WHERE a.studentid = b.studentid AND b.total_marks >
(SELECT total_marks
FROM marks
WHERE studentid = 'V002');
Example :-
Example :-
SELECT name, city, salary FROM ittutorial WHERE salary = (SELECT MAX(salary) FROM ittutorial);
Example :-
SELECT emp_name, city, income FROM employees emp WHERE income > ( SELECT AVG(income) FROM employees WHERE city = emp.city);
Example :-
SELECT department_id, AVG(SALARY) FROM EMPLOYEES GROUP BY department_id HAVING AVG(SALARY)>=ALL (SELECT AVG(SALARY) FROM EMPLOYEES GROUP BY department_id);
Example :-
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, job_id, department_id FROM employees E WHERE EXISTS (SELECT * FROM employees WHERE manager_id = E.employee_id);
Example :-
SELECT department_id, department_name FROM departments d WHERE NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM employees WHERE department_id = d.department_id);
Previous
Next
 What is MySql
What is MySql 