what is TRIGGER?
A mysql trigger is a stored database object that invoked automatically in response to an event such as insert, update, or delete that occurs in the associated table. For example, you can define a trigger that is invoked automatically before a new row is inserted into a table
File name : index.php
MySQL supports triggers that are invoked in response to the INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE event.
The SQL standard defines two types of triggers: row-level triggers and statement-level triggers.
A row-level trigger is activated for each row that is inserted, updated, or deleted. For example, if a table has 100 rows inserted, updated, or deleted, the trigger is automatically invoked 100 times for the 100 rows affected.
A statement-level trigger is executed once for each transaction regardless of how many rows are inserted, updated, or deleted.
MySQL supports only row-level triggers. It doesn’t support statement-level triggers.
Advantages of triggers
Triggers provide way to check the integrity of data.
Triggers handle errors from the database layer.
Triggers give an alternative way to run scheduled tasks. By using triggers, you don’t have to wait for the scheduled events to run because the triggers are invoked automatically before or after a change is made to the data in a table.
Triggers can be useful for auditing the data changes in tables.
Disadvantages of triggers
riggers can only provide extended validations, not all validations. For simple validations, you can use the NOT NULL, UNIQUE, CHECK and FOREIGN KEY constraints.
Triggers can be difficult to troubleshoot because they execute automatically in the database, which may not invisible to the client applications.
Triggers may increase the overhead of the MySQL Server.
CREATE TRIGGER
The CREATE TRIGGER statement creates a new trigger in mysql database.
{BEFORE | AFTER} {INSERT | UPDATE| DELETE }
ON table_name FOR EACH ROW
trigger_body;
First, specify the name of the trigger that you want to create after the CREATE TRIGGER keywords. Note that the trigger name must be unique within a database.
Next, specify the trigger action time which can be either BEFORE or AFTER which indicates that the trigger is invoked before or after each row is modified.
Then, specify the operation that activates the trigger, which can be INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE.
After that, specify the name of the table to which the trigger belongs after the ON keyword.
Finally, specify the statement to execute when the trigger activates. If you want to execute multiple statements, you use the BEGIN END compound statement.
The trigger body can access the values of the column being affected by the DML statement.
The following table illustrates the availability of the OLD and NEW modifiers:
Trigger Event OLD NEW
INSERT No Yes
UPDATE Yes Yes
DELETE Yes No
DEFINER :
definer is the user who is entitled with the privilege to perfor the trigger operations.
CREATE
[DEFINER = user] TRIGGER trigger_name
trigger_time trigger_event
ON tbl_name FOR EACH ROW
[trigger_order] trigger_body
trigger_name: trigger_name is the name of trigger instruction. This is a user-defined field.
trigger_time: trigger_time is the moment in which trigger is to be initiated. It is either BEFORE or AFTER indicating whether to perfor the trigger action before each row or after.
trigger_event: trigger_event is the change operation referred upon. INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE actions are used as triggers.
trigger_order: trigger order specifies if the trigger FOLLOWS or PRECEDES
trigger_body: trigger_body defines the trigger actions. If more than one statement is to be mentioned, it if preferred to use the BEGIN END block and also change the default delimiters.
DELIMITER $$
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name
trigger_time trigger_event
ON table_name FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
-- statements
END $$
DELIMITER;
The DEFINER clause specifies the MySQL account to be used when checking access privileges at trigger activation time. If a user value is given, it should be a MySQL account in 'user_name'@'host_name' format such as root@localhost
The user_name and host_name values both are required. CURRENT_USER also can be given as CURRENT_USER(). The default DEFINER value is the user who executes the CREATE TRIGGER statement.
Example
Employees Table
File name : employees.php
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
empno INT NOT NULL,
first_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
address VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
mobile VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL
);
table employees_audit
create a new table named employees_audit to keep the changes to the employees table
File name : employees_audit
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
empno INT NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
change_date DATETIME DEFAULT NULL,
action VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL
);
create trigger
create a BEFORE UPDATE trigger that is invoked before a change is made to the employees table
BEFORE UPDATE ON employees
FOR EACH ROW
INSERT INTO employees_audit
SET action = 'update',
empno = OLD.empno,
last_name = OLD.last_name,
change_date = NOW();
in body of the trigger, we used the OLD keyword to access values of the columns empno and last_name of the row affected by the trigger.
Show trigger in the database
File name : index.php
update a row in the employees table
SET
last_name = 'alam'
WHERE
empno = 101;
check table is updated ot not
query the employees_audit table to check if the trigger was fired by the UPDATE statement
Mysql BEFORE INSERT triggers
BEFORE INSERT triggers are automatically invoked before an insert event ouucrs on the table.
BEFORE INSERT
ON employees FOR EACH ROW
trigger_body;
First, specify the name of the trigger that you want to create
second, use BEFORE INSERT clause to specify the time to invoke the trigger
third, specify the name of the table that the trigger is associated with after the ON keyword
finally, specify the trigger body which contains one or more sql statements that execute when the trigger is invoked
Note: if you have multiple statements in the trigger_body, you have to use the BEGIN END block and change the default delimiter
CREATE TRIGGER mytrigger
BEFORE INSERT
ON employees FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
-- STATEMENTS---
END$$
DELIMITER ;
Note :-
BEFORE INSERT trigger, you can access and change the NEW values. However, you cannot access the OLD values because OLD values obviously do not exist.
create a BEFORE INSERT trigger to maintain a summary table from another table.
First Table :
File name : itechCenters.php
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
capacity INT NOT NULL
);
Second Table :
File name : itechCenterStats.php
totalCapacity INT NOT NULL
);
Creating BEFORE INSERT trigger
The following trigger updates the total capacity in the itechCenterStats table before a new work center is inserted into the itechCenters table
CREATE TRIGGER before_itechcenters_insert
BEFORE INSERT
ON itechCenters FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
DECLARE rowcount INT;
SELECT COUNT(*)
INTO rowcount
FROM itechCenterStats;
IF rowcount > 0 THEN
UPDATE itechCenterStats
SET totalCapacity = totalCapacity + new.capacity;
ELSE
INSERT INTO itechCenterStats(totalCapacity)
VALUES(new.capacity);
END IF;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
First, the name of the trigger is before_itechcenters_insert specified in the CREATE TRIGGER clause:
CREATE TRIGGER before_itechcenters_insert
Second, the triggering event is: BEFORE INSERT
Third, the table that the trigger associated with is itechCenters table:
ON itechCenters FOR EACH ROW
Finally, inside the trigger body, we check if there is any row in the itechCenterStats table.
If the table itechCenterStats has a row, the trigger adds the capacity to the totalCapacity column. Otherwise, it inserts a new row into the itechCenterStats table.
Test the MySQL BEFORE INSERT trigger
insert a new row into the itechCenter table
Second, query data from the itechCenterStats table:
The trigger has been invoked and inserted a new row into the itechCenterStats table.
Third, insert a new record in itechCenters table:
Finally, query data from the itechCenterStats:
SELECT * FROM itechCenterStats;
MySQL AFTER INSERT Trigger
MySQL AFTER INSERT trigger to insert data into a table after inserting data into another table.
MySQL AFTER INSERT triggers are automatically invoked after an insert event occurs on the table.
AFTER INSERT
ON table_name FOR EACH ROW
trigger_body
First, specify the name of the trigger that you want to create after the CREATE TRIGGER keywords.
Second, use AFTER INSERT clause to specify the time to invoke the trigger.
Third, specify the name of the table on which you want to create the trigger after the ON keyword.
Finally, specify the trigger body which consists of one or more statements that execute when the trigger is invoked.
In case the trigger body has multiple statements, you need to use the BEGIN END block and change the default delimiter:
DELIMITER $$
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name
AFTER INSERT
ON table_name FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
-- statements
END$$
DELIMITER ;
In an AFTER INSERT trigger, you can access the NEW values but you cannot change them. Also, you cannot access the OLD values because there is no OLD on INSERT triggers.
MySQL AFTER INSERT trigger example
First Table :
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(255),
birthDate DATE,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
Second tabel :
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
memberId INT,
message VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id , memberId)
);
Creating AFTER INSERT trigger example
CREATE TRIGGER after_members_insert
AFTER INSERT
ON members FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
IF NEW.birthDate IS NULL THEN
INSERT INTO reminders(memberId, message)
VALUES(new.id,CONCAT('Hi ', NEW.name, ', please update your date of birth.'));
END IF;
END$$
DELIMITER ;
In this trigger:
First, the name of the trigger is after_members_insert specified in the CREATE TRIGGER clause:
CREATE TRIGGER after_members_insert
Second, the triggering event is:
AFTER INSERT
Third, the table that the trigger associated with is members table:
ON members FOR EACH ROW
Finally, inside the trigger body, insert a new row into the reminder table if the birth date of the member is NULL.
Testing the MySQL AFTER INSERT trigger
First, insert two rows into the members table:
VALUES
('sana', 'sana@rahatfoundarion.in', NULL),
('mahi', 'mahi@rahatfoundation.in','2000-01-01');
Second, query data from the members table:
File name : index.php
Third, query data from reminders table:
File name : index.php
We inserted two rows into the members table. However, only the first row that has a birth date value NULL, therefore, the trigger inserted only one row into the reminders table.
File name : index.php
File name : index.php
File name : index.php
MySQL DROP TRIGGER
The DROP TRIGGER statement deletes a trigger from the database.
File name : index.php
SHOW TRIGGERS;
DROP TRIGGER before_billing_update;
SHOW TRIGGERS;
File name : index.php
File name : index.php
MySQL BEFORE UPDATE Trigger
MySQL BEFORE UPDATE triggers are invoked automatically before an update event occurs on the table associated with the triggers.
syntax :
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name
BEFORE UPDATE
ON table_name FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
-- statements
END$$
DELIMITER ;
In a BEFORE UPDATE trigger, you can update the NEW values but cannot update the OLD values.
MySQL BEFORE UPDATE trigger example
create sales table :
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
product VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
quantity INT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
fiscalYear SMALLINT NOT NULL,
fiscalMonth TINYINT NOT NULL,
CHECK(fiscalMonth >= 1 AND fiscalMonth <= 12),
CHECK(fiscalYear BETWEEN 2000 and 2050),
CHECK (quantity >=0),
UNIQUE(product, fiscalYear, fiscalMonth),
PRIMARY KEY(id)
);
Insert record
Second, insert some rows into the sales table:
VALUES
('2003 Harley-Davidson Eagle Drag Bike',120, 2020,1),
('1969 Corvair Monza', 150,2020,1),
('1970 Plymouth Hemi Cuda', 200,2020,1);
SELECT * FROM sales;
Creating BEFORE UPDATE trigger
CREATE TRIGGER before_sales_update
BEFORE UPDATE
ON sales FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
DECLARE errorMessage VARCHAR(255);
SET errorMessage = CONCAT('The new quantity ',
NEW.quantity,
' cannot be 3 times greater than the current quantity ',
OLD.quantity);
IF new.quantity > old.quantity * 3 THEN
SIGNAL SQLSTATE '45000'
SET MESSAGE_TEXT = errorMessage;
END IF;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
Note : The trigger is automatically fired before an update event occurs for each row in the sales table.
If you update the value in the quantity column to a new value that is 3 times greater than the current value, the trigger raises an error and stops the update.
File name : index.php
Testing the MySQL BEFORE UPDATE trigger
SET quantity = 150
WHERE id = 1;
SELECT * FROM sales;
File name : index.php
SET quantity = 500
WHERE id = 1;
File name : index.php
Error Code: 1644. The new quantity 500 cannot be 3 times greater than the current quantity 150
File name : index.php
MySQL AFTER UPDATE Trigger
MySQL AFTER UPDATE triggers are invoked automatically after an update event occurs on the table associated with the triggers
syntax:
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name
AFTER UPDATE
ON table_name FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
-- statements
END$$
DELIMITER ;
In a AFTER UPDATE trigger, you can access OLD and NEW rows but cannot update them.
MySQL AFTER UPDATE trigger example
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
product VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
quantity INT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
fiscalYear SMALLINT NOT NULL,
fiscalMonth TINYINT NOT NULL,
CHECK(fiscalMonth >= 1 AND fiscalMonth <= 12),
CHECK(fiscalYear BETWEEN 2000 and 2050),
CHECK (quantity >=0),
UNIQUE(product, fiscalYear, fiscalMonth),
PRIMARY KEY(id)
);
File name : index.php
VALUES
('2001 Ferrari Enzo',140, 2021,1),
('1998 Chrysler Plymouth Prowler', 110,2021,1),
('1913 Ford Model T Speedster', 120,2021,1);
SalesChanges Table
File name : index.php
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
salesId INT,
beforeQuantity INT,
afterQuantity INT,
changedAt TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
File name : index.php
CREATE TRIGGER after_sales_update
AFTER UPDATE
ON sales FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
IF OLD.quantity <> new.quantity THEN
INSERT INTO SalesChanges(salesId,beforeQuantity, afterQuantity)
VALUES(old.id, old.quantity, new.quantity);
END IF;
END$$
DELIMITER ;
update
File name : index.php
File name : index.php
File name : index.php
File name : index.php
Trigger Example :-
AFTER UPDATE ON `table_1`
FOR EACH ROW
INSERT INTO table_2 (SELECT * FROM table_1)
How to create trigger?
First create a table on which you apply trigger.
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
`title` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`author` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`created_at` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
`updated_at` datetime DEFAULT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE `tutorial_log` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
`tutorial_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`action` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`date` datetime DEFAULT NULL
);
create trigger on above table tutorial
this trigger insert row in tutorial_log table after insert data in tutorial table.
CREATE TRIGGER `tutorial_trigger` AFTER INSERT ON `tutorial` FOR EACH ROW insert into tutorial_log values(null,new.id,'Inserted',now())
$$
DELIMITER ;
how to create trigger on localhost
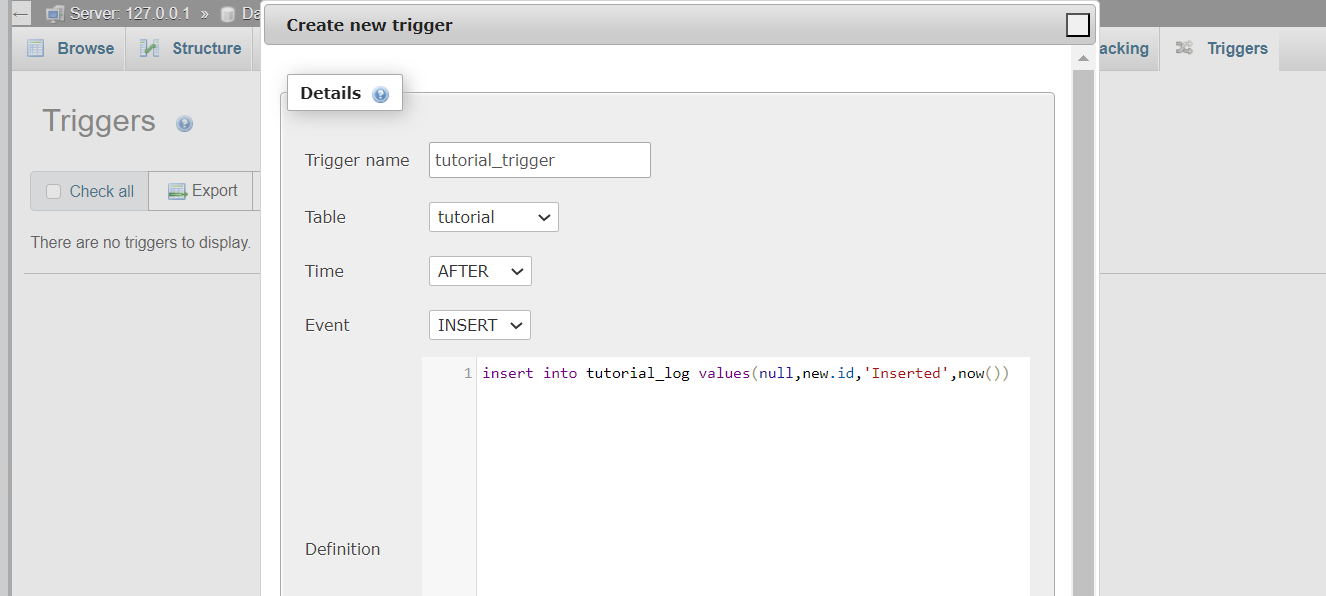
After Update tutorial table trigger fire on tutorial_log table.
File name : index.php
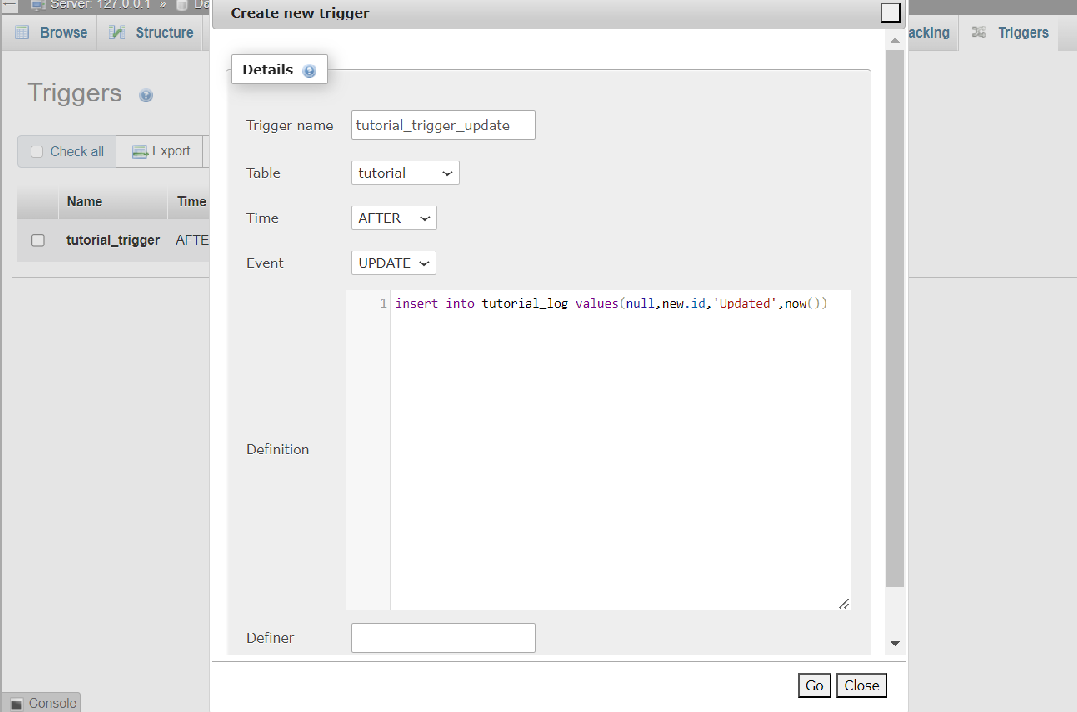
trigger fire before delete record from tutorial table.
Insert trigger
Declare docID INT;
Declare doc_status INT;
SET docID = (SELECT max(i_doc_no) FROM table1 );
INSERT INTO table2 SET fki_doc_id = docID;
SET doc_status = (SELECT fki_status FROM table1 WHERE doc_no=docID);
INSERT INTO table3
SET doc_no = docID,
doc_status = doc_status
END
Example
INSERT INTO archive_table(
id,
agenda_id,
meeting_id,
agenda_info,
created_at,
created_by,
status) VALUES (
NULL,
old.id,
old.meeting_id,
old.agenda_info,
old.created_at,
old.created_by,
old.status
NOW()
);
END
Example
Previous Next
Trending Tutorials
0.0 / 5
0 Review
 What is MySql
What is MySql 